FAQ on Pathologic calcification-Dystrophic calcification-metastatic calcification-Psammoma body
FAQ on Pathologic calcification:
In this blog I will discuss about Pathologic calcification,types, dystrophic calcification, psammoma body, difference between dystrophic and metastatic calcification and causes of calcification in liver,lung,kidney,prostate and bone.
Q1: Define Pathologic calcification.
Ans:
PATHOLOGIC CALCIFICATION:
Pathologic Calcification is a process by which calcium salts are deposited in tissues other than osteoid or enamel.This type of Calcification is usually associated with deposition of small quantity of iron, magnesium and other elements.Where as physiological Calcification occurs in osteoid(bone) and enamel of our body.
Figure:Pathologic calcification
Q 2: What are the types of Pathologic calcification?
Ans : Pathologic calcification is classified into two types: 1) dystrophic calcification and 2) metastatic calcification.
Figure:Types of Pathologic calcification
Q 3: What is dystrophic calcification?
Ans: DYSTROPHIC CALCIFICATION:
Dystrophic calcification is defined as deposition of calcium salts in dead/degenerated or dying tissue when calcium metabolism and serum calcium level are normal.
 |
| Figure: Dystrophic calcification |
Examples:
Dystrophic calcification in dead tissue:
a) Caseous necrosis: Dystrophic calcification can occur in focus of longstanding Caseous necrosis.
b) Liquefactive necrosis: Dystrophic calcification can occur in longstanding abscess also.
c) Infarction: After infarction, dead tissues can undergo dystrophic calcification.
d) Gamma-Gandy bodies: Due to chronic venous congestion,there is deposition of calcium salts along with hemosiderin in the fibrous tissue of spleen.
e) Thrombi: Old thrombi in veins may produce calcification.
f) Congenital toxoplasmosis involving central nervous system(CNS) may lead to dystrophic calcification.
g) Fat necrosis: Fat necrosis following acute pancreatitis or trauma to breast can cause dystrophic calcification.
Dystrophic calcification in dying/degenerating tissue:
a) Hyaline degeneration followed by calcification can occur in old scars.
b) Atheroma: In aorta or coronary artery can undergo calcification.
c) Cyst wall can show calcification.
d) Psammoma body: Concentric lamellar deposition of calcium salts(will be discussed in detail below).
e) Calcinosis cutis: Irregular nodular deposits of calcium in skin and subcutaneous tissue.
f) Senile degeneration.
g) Monckeberg arteriosclerosis(will be discussed in detail below).
Also you can watch this video on distrophic calcification:
Q 4: What is metastatic calcification?
Ans:
METASTATIC CALCIFICATION:
Metastatic calcification is the deposition of calcium salts in normal tissue due to high serum calcium level. It is observed because of deranged calcium metabolism, decreased excretion, increased absorption of calcium. Metastatic calcification commonly involve the following tissues:
- Alveolar septa of Lung.
- The basement membrane of renal tubules.
- Internal elastic lamina of systemic arteries and pulmonary vein.
- Gastric mucosa.
Examples of metastatic calcification:
a) Hyperparathyroidism: There is increased resorption of bones resulting in hypercalcemia. As a result,there is metastatic calcification.
b) Paraneoplastic syndrome: Due to the secretion of the parathyroid hormone-related protein.
c) Resorption of bone due to:
- Multiple myeloma,leukaemia.
- Tumor metastasis to bone.
- Paget's disease of bone.
- Immobilization.
d) Vitamin D related disorders:
- Vitamin D intoxication.
- William's syndrome.
- Sarcoidosis.
You can also watch this video on Metastatic calcification:
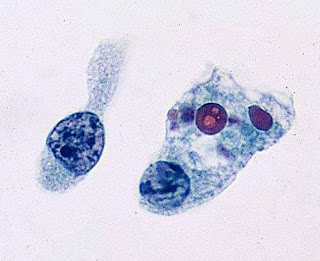
Q 4: What are Psammoma bodies?
Figure:Psammoma body
Ans: Psammoma bodies are concentric lamellated calcified structures found in various neoplastic as well as non- neoplastic conditions. Psammoma bodies are thought to arise from infarction and subsequent calcification of any papillary structure.
Psammoma bodies can be observed in following conditions:
1. Papillary thyroid carcinoma.
2. Papillary renal cell carcinoma.
3. Papillary serous carcinoma of endometrium.
4. Meningioma.
5. Papillary serous cystadenoma and cystadenocarcinoma of ovary.
6. Mesothelioma.
7. Micropapillary subtype of lung adenocarcinoma.
8. Prolactinoma.
9.Somatostatinoma.
10. Endosalpingiosis..... etc.
Q 5: Difference between Dystrophic and Metastatic calcification.
Ans:
Figure: Difference between dystrophic and metastatic calcification.
Q 6:Visit What are the causes of calcification in liver?
Ans: Calcification in liver may be due to various causes such as-
- Tuberculosis
- Echinococcus cyst
- Large hemangioma
- Hepatic adenoma
- Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
So,there are different causes behind hepatic calcification. Most often hepatic calcification is incidentally detected on radiological investigations like CT scan, MRI etc. To detect the cause behind calcification other investigations like FNAC, biopsy,biochemical analysis need to be done.
Q 7: What are the causes of calcification in lung?
Ans: Most often calcifications are found in lung in chest x-ray or CT scan.Both dystrophic and metastatic calcification can occur in lung.
In following cases calcification is commonly observed in lung:
- Healed primary tuberculosis- most common cause of calcification in lung.
- Old histoplasmosis- Infection by organism Histoplasma capsulatum.
- Pneumocystis carinii infection.
- Old hematoma- In the centre of old hematoma- there may be gradual calcification.
- Old infarct in lung may eventually get calcified.
- Pleural calcification can occur after hemothorax or empyema.
- Also echinococcus cyst in lung can eventually get calcified.
Q 8: What are the causes of calcification in kidney?
Ans: Deposition of calcium in kidney is known as nephrocalcinosis,it is due to following reasons:
- Primary hyperparathyroidism.
- Vitamin D therapy.
- Sarcoidosis etc.
Q 9: What are the causes of calcification in Prostate?
Ans: Most common cause of prostatic calcification is ideopathic,that means the reason is unknown. But the conditions secondary to which calcification in Prostate can occur are:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Tuberculosis
- Bacterial prostatitis
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia(BHP)
- Prostatic carcinoma
- Radiation therapy
Q 10: What is calcification of bone?
Ans: Deposition of calcium salts in bone is known as calcification of bone. Normally calcification of bone tissue occur during development,but calcification in tissues other than bone commonly occur in abnormal conditions.
Visit our website homepage for more articles on Pathology👇
www.pathologydiscussion.com
Feel free to share any of our articles on social media(Directly from the website) if you find it helpful. Thank you!!!!





Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for posting your comment.Your question will be answered soon.