Pathology MCQ6
Pathology MCQ6:
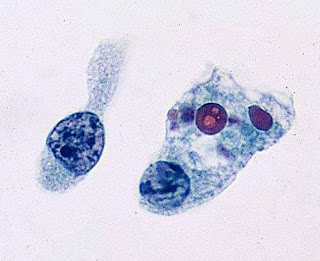
A 59-year-old woman with hyperlipidemia has had anginal pain for the past 24 hours. Laboratory findings show no increase in serum troponin I or creatine kinase–MB. She is
in stable condition 2 weeks later and has no chest pain, but a small artery in the epicardium has undergone the changes seen in the figure. Which of the following terms best describes this finding in this epicardial artery?
A Air embolus
B Cholesterol embolization
C Chronic passive congestion
D Fat embolism syndrome
E Mural thrombosis
F Organization with occlusion
G Phlebothrombosis
Explanation:
The figure shows an organizing thrombus in a small artery. Such a peripheral arterial occlusion was insufficient to produce infarction, as evidenced by the lack of enzyme elevation. Thrombi become organized over time if they are not dissolved by fibrinolytic activity. After a thrombus has formed, it may become organized with ingrowth of capillaries, fibroblast proliferation, and macrophage infiltration, which eventually clears part or most of the clot; there can be formation of one or more new lumens (recanalization). Air emboli are uncommon and usually the result of trauma. Air emboli on the arterial side can cause ischemia through occlusion even when very small, whereas on the venous side, more than 100 mL of air trapped in the heart may reduce cardiac output. When gases that became dissolved in tissues at high pressure bubble out at decompression with lower pressure in blood and tissues, then air emboli form. Cholesterol emboli can break off from atheromas in arteries and proceed distally to occlude small arteries; however, because these emboli are usually quite small, they are seldom clinically significant. Chronic passive congestion refers to capillary, sinusoidal, or venous stasis of blood within an organ such as the lungs or liver. Fat emboli are globules of lipid that are most likely to form after traumatic injury, typically to long bones. Mural thrombi are thrombi that form on the surfaces of the heart or large arteries. So, the correct option is optionF(Photo credit:Pinterest)
A 59-year-old woman with hyperlipidemia has had anginal pain for the past 24 hours. Laboratory findings show no increase in serum troponin I or creatine kinase–MB. She is
in stable condition 2 weeks later and has no chest pain, but a small artery in the epicardium has undergone the changes seen in the figure. Which of the following terms best describes this finding in this epicardial artery?
A Air embolus
B Cholesterol embolization
C Chronic passive congestion
D Fat embolism syndrome
E Mural thrombosis
F Organization with occlusion
G Phlebothrombosis
Explanation:
The figure shows an organizing thrombus in a small artery. Such a peripheral arterial occlusion was insufficient to produce infarction, as evidenced by the lack of enzyme elevation. Thrombi become organized over time if they are not dissolved by fibrinolytic activity. After a thrombus has formed, it may become organized with ingrowth of capillaries, fibroblast proliferation, and macrophage infiltration, which eventually clears part or most of the clot; there can be formation of one or more new lumens (recanalization). Air emboli are uncommon and usually the result of trauma. Air emboli on the arterial side can cause ischemia through occlusion even when very small, whereas on the venous side, more than 100 mL of air trapped in the heart may reduce cardiac output. When gases that became dissolved in tissues at high pressure bubble out at decompression with lower pressure in blood and tissues, then air emboli form. Cholesterol emboli can break off from atheromas in arteries and proceed distally to occlude small arteries; however, because these emboli are usually quite small, they are seldom clinically significant. Chronic passive congestion refers to capillary, sinusoidal, or venous stasis of blood within an organ such as the lungs or liver. Fat emboli are globules of lipid that are most likely to form after traumatic injury, typically to long bones. Mural thrombi are thrombi that form on the surfaces of the heart or large arteries. So, the correct option is optionF(Photo credit:Pinterest)
Visit our website homepage for more articles on Pathology👇
www.pathologydiscussion.com
Feel free to share any of our articles on social media(Directly from the website) if you find it helpful. Thank you!!!!
www.pathologydiscussion.com
Feel free to share any of our articles on social media(Directly from the website) if you find it helpful. Thank you!!!!


Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for posting your comment.Your question will be answered soon.