Pathogenesis of fatty liver
Pathogenesis of Fatty Liver:
Fatty liver is a condition where there is abnormal accumulation lipids(triglyceride) in the cytosol of hepatocytes.Various mechanisms are involved in excess accumulation of triglyceride in the liver and one or
more mechanism may be responsible:
1. Excessive entry of free fatty acids (FFA) into the liver from peripherals stores. FFA enters into liver during starvation and diabetes.
2. Defective metabolism of lipids: This may be due to:
a. Increased synthesis of fatty acids by liver.
b. Decreased oxidation of fatty acids into ketone bodies resulting in increased
esterification of fatty acids into triglycerides. Hypoxia inhibits fatty acid oxidation.
c. Decreased synthesis of apoproteins (e.g. in CCl4 and protein malnutrition) causes
decreased formation of lipoproteins from triglycerides.
3. Defective excretion of lipoproteins: Fatty liver may also develop due to defect in excretionl ipoproteins from liver into the blood.
Above mentioned facts are responsible for developement of fatty liver.(P.C-webpath)
Visit our website homepage for more articles on Pathology👇
www.pathologydiscussion.comFeel free to share any of our articles on social media(Directly from the website) if you find it helpful. Thank you!!!!
Fatty liver is a condition where there is abnormal accumulation lipids(triglyceride) in the cytosol of hepatocytes.Various mechanisms are involved in excess accumulation of triglyceride in the liver and one or
more mechanism may be responsible:
 |
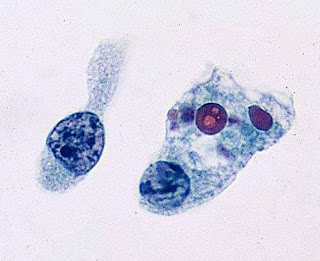
| Figure: Fatty liver histology |
1. Excessive entry of free fatty acids (FFA) into the liver from peripherals stores. FFA enters into liver during starvation and diabetes.
2. Defective metabolism of lipids: This may be due to:
a. Increased synthesis of fatty acids by liver.
b. Decreased oxidation of fatty acids into ketone bodies resulting in increased
esterification of fatty acids into triglycerides. Hypoxia inhibits fatty acid oxidation.
c. Decreased synthesis of apoproteins (e.g. in CCl4 and protein malnutrition) causes
decreased formation of lipoproteins from triglycerides.
 |
| Figure: Fatty liver microscopy |
 |
| Figure: Fatty liver gross picture |
Visit our website homepage for more articles on Pathology👇
www.pathologydiscussion.comFeel free to share any of our articles on social media(Directly from the website) if you find it helpful. Thank you!!!!

Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for posting your comment.Your question will be answered soon.