Whipple disease
Whipple disease:
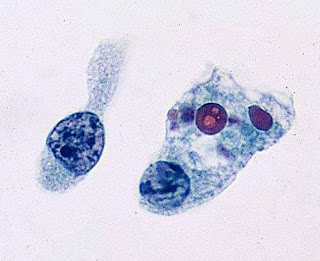
The cytoplasm of the macrophages in Whipple disease contains intensely PAS-positive material(arrow) that is coarsely granular.

Whipple disease, a chronic systemic illness with numerous gastrointestinal features such as diarrhea and malabsorption, is caused by Tropheryma whippleii, a rod-shaped microorganism . The diagnosis of Whipple disease is usually based on the identification of PAS-positive, diastase-resistant inclusions in small-intestinal biopsy specimens. The diagnosis can be confirmed by a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay for the bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA , by electron microscopy, or by immunohistochemistry (IHC) . The organism has been cultured . Whipple disease responds dramatically to antibiotic therapy; without treatment, it is fatal . The characteristic histopathology of Whipple disease is the infiltration of various organs with macrophages containing the T. whippleii bacillus. This infiltration has a predilection for the lamina propria of the small intestine, the mesenteric lymph nodes, the cardiac valves, and the central nervous system.
If you like, you can visit our youtube channel and facebook page👇🏻
Youtube channel link-https://m.youtube.com/channel/UCPGvHc5Ttw4EtB72WVMiYSw/videos
Facebook page link-https://m.facebook.com/PathologyDiscussionForum/?ref=bookmarks
The cytoplasm of the macrophages in Whipple disease contains intensely PAS-positive material(arrow) that is coarsely granular.

Whipple disease, a chronic systemic illness with numerous gastrointestinal features such as diarrhea and malabsorption, is caused by Tropheryma whippleii, a rod-shaped microorganism . The diagnosis of Whipple disease is usually based on the identification of PAS-positive, diastase-resistant inclusions in small-intestinal biopsy specimens. The diagnosis can be confirmed by a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay for the bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA , by electron microscopy, or by immunohistochemistry (IHC) . The organism has been cultured . Whipple disease responds dramatically to antibiotic therapy; without treatment, it is fatal . The characteristic histopathology of Whipple disease is the infiltration of various organs with macrophages containing the T. whippleii bacillus. This infiltration has a predilection for the lamina propria of the small intestine, the mesenteric lymph nodes, the cardiac valves, and the central nervous system.
If you like, you can visit our youtube channel and facebook page👇🏻
Youtube channel link-https://m.youtube.com/channel/UCPGvHc5Ttw4EtB72WVMiYSw/videos
Facebook page link-https://m.facebook.com/PathologyDiscussionForum/?ref=bookmarks
Follow our facebook page for recent articles/videos 😎

Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for posting your comment.Your question will be answered soon.