Commonly asked qiestions about Hyaline change
Hyaline change:
Q1: Define Hyaline change.
Ans: Hyaline change can be defined as any change in intracellular or extracellular environment giving rise to pink, homogenous and glossy appearance of the tissue in H /E stained sections.
It is most commonly associated with amyloid or amyloid-like protein deposition in tissue.
Q2: What are the types of Hyaline change?
Ans: There are two types of Hyaline change. i) Intracellular & ii) Extracellular.
Q3: What is intracellular Hyaline change?
Ans: There is a deposition of Hyaline material within the cytoplasm.Examples:
Q1: Define Hyaline change.
Ans: Hyaline change can be defined as any change in intracellular or extracellular environment giving rise to pink, homogenous and glossy appearance of the tissue in H /E stained sections.
It is most commonly associated with amyloid or amyloid-like protein deposition in tissue.
Q2: What are the types of Hyaline change?
Ans: There are two types of Hyaline change. i) Intracellular & ii) Extracellular.
Q3: What is intracellular Hyaline change?
Ans: There is a deposition of Hyaline material within the cytoplasm.Examples:
- Mallory body:
It is also known as Mallory-Denk body and Mallory's Hyaline. It is found in hepatocytes and comprised of damaged intermediate filaments within the cytoplasm. Mallory bodies are commonly found in the case of alcoholic liver disease. But, it can also be found in the following conditions:
Figure: Mallory-Denk body
- Cirrhosis
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Wilson's disease
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Morbid obesity
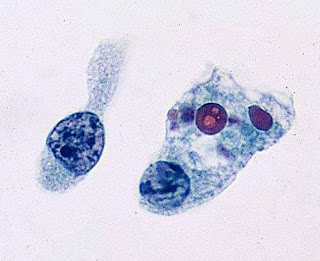
- Russell body:
Russel bodies are due to excessive accumulation of immunoglobulins in the cytoplasm of plasma cells. These structures appear as eosinophilic large homogenous globules in the cytoplasm of plasma cells. Russel bodies are actually distended endoplasmic reticulum. These are produced due to failure of the excretion of immunoglobulins while the production is normal. These excess immunoglobulins are stored in ER causing distension of ER. Russell bodies are found to be positive with PAS, CD 38, CD 138. If one cell has multiple Russell bodies, then that cell is known as" Mott cell".
Figure: Russell body - Crooke's hyaline: Deposition of hyaline material in the pituitary gland.
- Zenker's hyaline change: It occurs
In the case of muscle necrosis in acute infectious disease. Commonly observed muscles are rectus abdominis and diaphragm. It is a type of coagulative necrosis.
Figure: Hyaline change in leiomyoma
Q4: What is the extracellular hyaline change?
Ans: Deposition of hyaline material is found in the following conditions:
- Old scars: There is the deposition of hyaline tissue in scars.
- Hyaline change in leiomyoma
- The hyaline membrane in newborn
- Corpora amylecia in the prostate, old infarct of the lung.
- Hyaline arteriosclerosis
- Hyalinization of glomeruli in chronic glomerulonephritis




Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for posting your comment.Your question will be answered soon.